Articles
Types of Breast Implants
How is breast augmentation performed?
Breast augmentation is the enhancement of the breast size as well as shape. In modern plastic surgery, this can be performed with breast implants or through fat grafting. By choosing the correct technique, a beautiful, aesthetically pleasing, and naturally feeling breast can be achieved.
Breast Implants
Breast implants have been the mainstay of breast augmentation for decades and have undergone multiple evolutionary developments. They are the most efficient way of enhancing the breast in a single stage, to achieve the particular outcome desired. Through the years, they have also proven to be very safe, and if done well, can last a lifetime. Most of the breast implants used nowadays are made of a durable silicone outer shell and an inner softer silicone core. They can be inserted either above or below the chest muscle for camouflage depending on the amount of existing breast tissue, and the scars can be well hidden in the breast fold or axillary region. For implants placed under the chest muscle, the advanced dual-plane techniques have allowed for a naturally appearing lower part of the breast whilst affording adequate coverage at the upper part of the breast.
Fat Grafting
Fat grafting involves the harvest of fat using liposuction techniques from areas of the body with unwanted fats and injecting the fat carefully into the breast to augment its size. It is the most natural way of enhancement and does not carry the associated risks of implant insertion. However, there is a limitation to the amount of fat that can be injected at each sitting. These limitations include the amount of existing breast tissue that can accept the fat, which has to be able to pick up a new blood supply, as well as the amount of fat available for harvest. Fat grafting sessions can, however, be repeated 3-6 months apart.
Hybrid Technique
In certain cases, both techniques can be combined in what has been termed a hybrid breast augmentation. This allows the increase of size afforded by the implant, while fat grafting is used to finesse the necessary areas and to also buffer any areas lacking in breast implant soft tissue coverage.
Why are there so many different types of breast implants?
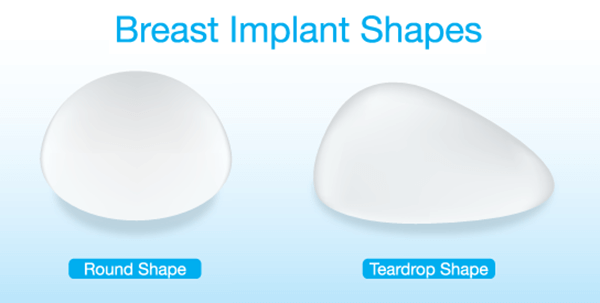
Breast implants come in many sizes, with two basic shapes: round or tear-drop. The variety of breast implants reflects the need to accommodate the differences between individuals, including body shape, weight, and height. The type of breast implant chosen is dependent on the desired final outcome that fits with the woman’s existing breast tissue characteristics to achieve a natural, enhanced, and long-lasting outcome. For example, an implant that is too big for the existing breast tissue can cause over-stretching of the skin, and premature aging of the breasts.
Tear-drop Shape Implants
Tear-drop breast implants have a more anatomical shape, resembling the normal breast, with more of the volume at the bottom of the implant. However, if the implant rotates in the created pocket, it can lead to obvious malposition deformity. This can be mitigated by creating a well-fitting pocket during breast augmentation surgery.
Round Shape Implants
Round breast implants have the advantage of maintaining their shape in the pocket in which they are placed. This leads to no risk of rotation deformity. However, as the peak of the implant is right in the middle, it will give a fuller appearance in the upper part of the breast.
In recent years, technological advances in silicone gel technology have allowed for a more natural feel and flow of the gel within the implant shell. This means that a round implant can more closely resemble an anatomical implant, without its associated malposition risks.
What is texture in breast implants?
Breast implant types can also be classified into smooth or textured-coated implants. Textured implants have a rough coating on the shell surface, which helps with reducing rotation as well as capsular contracture. However, in recent years, textured implants have been associated with a form of lymphoma, more of which will be discussed later. Smooth implants, as the name implies, have no coating, and have a higher risk of malposition. However, this risk is minimized in smooth round implants.
More recent technological advancements include nano-textured implants, which are purported to carry less risk of biofilm and lymphoma while minimizing the drawbacks of smooth implants.
How do I choose the right size for my breast implants?
In terms of size, breast implants come in different volumes which dictate the width and height of the implants. The volume chosen is dependent on the existing body shape of the patient, as well as the desired cup size. In general, each cup size is equivalent to 150-175cc of volume.
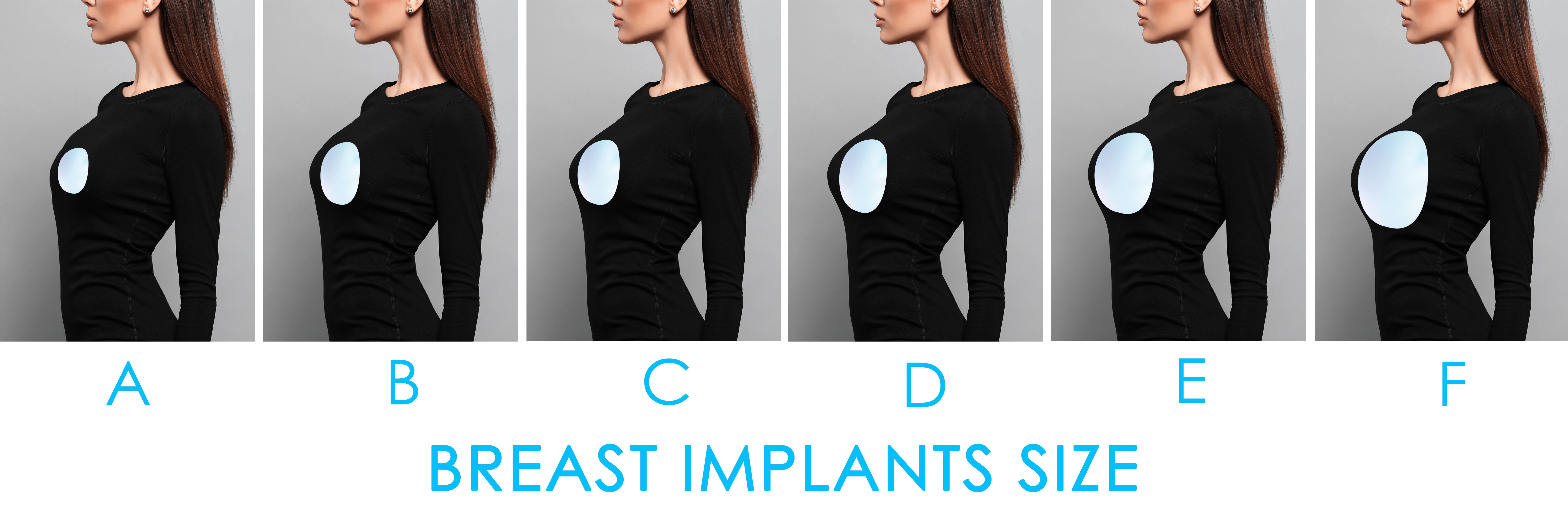
Together with your plastic surgeon, there are visual aids that can help you decide which volume of the implant to go for. These include the use of ‘dummy’ implants placed in a bra in front of a mirror or computer software that can simulate your breast augmentation outcome. Remember, whilst most women would think that bigger is better, implants that are too large for your frame can lead to over-stretching of your existing skin, neck ache and result in visibility of the implant with time.
For the cases of breast reconstruction, the type and size of breast implants are to be chosen in consideration of the planned technique to be applied.
What are the complications of breast implants?
Carefully inserted, breast implant complications can be minimized. This includes precise pocket creation, antibiotic use, and a sterile, no-touch technique. The main risk of breast implants is infection. In the early stage, this can manifest as cellulitis or discharge from the breast insertion site. Mild infections can be treated with antibiotic therapy, while more serious infections may require breast implant removal. In the later stages, a low-level infection can lead to biofilm formation, which is responsible for the development of capsular contracture. Whilst every breast implant will eventually form a capsule, capsular contracture is the hardening of this capsule, which can lead to distortion, pain in the breast, and necessitate breast implant exchange. Another complication of biofilm formation is the development of breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL). This is rare cancer that has been associated with textured breast implants, due to their larger surface area for infection. The risk of BIA-ALCL is about 1:10000 women with breast implants and is curable.
Other complications of breast implant insertion include visible scarring at the implant insertion site, rippling due to inadequate soft tissue coverage, asymmetry, as well as implant rupture. With proper selection and technique, these are avoidable.
For more information, do schedule an appointment with a qualified, board-certified plastic surgeon, who can go through your options and develop the best treatment plan to suit you.
Contact Form
1 Orchard Boulevard #10-08 Camden Medical Centre, Singapore 248649
6 Napier Rd, #08-01 Gleneagles Medical Center, Singapore 258499
Tel: +65 6737 4565 | Mobile: +65 8828 4565 | Email: clinic@polarisplasticsurgery.com | Business Hours: Mon - Fri: 9am - 6pm | Sat: 9am - 1pm | Sun/Ph: Closed