Reconstructive Procedures: Extremity Reconstruction
Extremity Reconstruction
Why do people need extremity reconstruction?
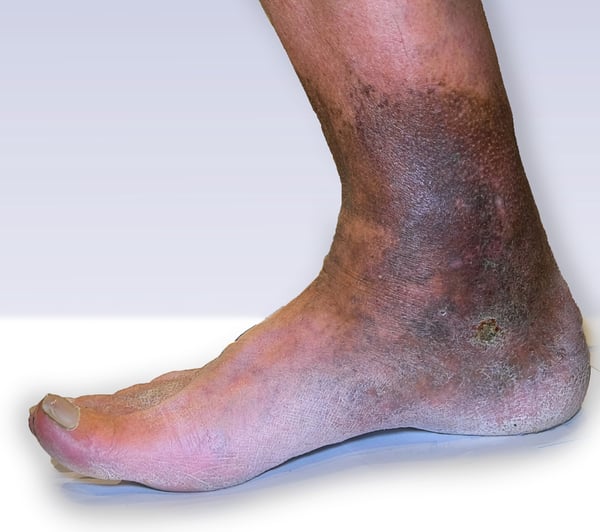
Wounds of the extremities can occur due to multiple reasons including trauma, infection, and cancer excision. Patients with diabetes and peripheral vascular disease are also very prone to developing wounds of the extremities, particularly the feet.
The resultant defects vary in size, depth, and tissue involved, and can be debilitating and disfiguring, resulting in loss of function in the arm or the leg. Moreover, they often cannot be simply sutured closed, and if left open, will take a long time to heal and can be prone to infection.
Reconstructive surgery of the extremities aims to restore form and function to the patient by anatomical restoration of skin, muscle, and bone, with the goal of replacing like with like as much as possible and allowing the patient to return to normal activity early.
How is extremity reconstruction performed?
Once the wound is ready, your plastic surgeon will utilize the armamentarium of the reconstructive elevator with the goals of functional as well as aesthetic reconstruction. This may involve the use of tissue expansion, grafts, or flaps. Grafts are performed when the wound bed has an adequate blood supply, while flaps are performed as local, perforator-based, pedicled or free flaps, depending on the extent of the defect and the complexity of surgery.
What happens before surgery?
You may be required to see an anaesthetist, and blood tests and other investigations to determine your suitability for anaesthesia may be performed.
If your extremity reconstruction is performed in relation to cancer removal, you may require neo-adjuvant treatments such as radiotherapy or chemotherapy. Your cancer surgeon will discuss this with you.
During the procedure
Post-operative care
Once the reconstruction is stable at about 1 week after surgery, you will be started on dangling exercises and partial weight bearing with a pressure garment. This involved periodic lowering of the limb to enable training of the reconstruction to accept the effects of gravity. For both the upper and lower extremity, there will be a period of a few weeks where rehabilitation is required. Most patients can get back to full function/full weight bearing of the lower extremity at about 4 weeks after surgery.
If your extremity reconstruction is performed in relation to cancer removal, you may require adjuvant treatments such as radiotherapy or chemotherapy. Your cancer surgeon will discuss this with you.
Potential risks and complications
For the extremities, the reconstruction can be slightly bulky in the initial few months. This bulk can be managed with a small debulking procedure. This is especially pertinent to the lower extremity around the foot and ankle area, where footwear is concerned.
Why choose Polaris Plastic Surgery?
Schedule a consultation with one of our surgeons to assess your needs and goals. He will communicate with you regarding your concerns, and in discussion with you, formulate a plan to perform the appropriate reconstructive procedure.
FAQ
Can extremity reconstruction be performed for diabetic patients?
Diabetic patients and those with peripheral vascular disease are more prone to developing wounds of the extremities, especially the lower extremity. This is due to reduced blood supply, along with loss of sensation to the toes, feet, and ankles. Left untreated, these wounds often get infected or turn gangrenous. Adequate early management along with diabetic control is key to prevention of complications. Established wounds can also be treated with a combination of debridement, special dressings, and potential reconstruction. This is a carefully mapped-out process which can involve multiple specialties including plastic surgeons, orthopaedic surgeons, vascular surgeons, and podiatrists. As the wound expert, the plastic surgeon is well placed to manage these wounds.
How soon can I get back to normal function after extremity reconstruction?
Return to function for extremity wounds is variable and depends on the extent and tissues involved. In a pure soft tissue wound, return to full weight bearing for the lower extremity can occur in about 3 to 4 weeks after surgery. If there is bony fracture fixation or reconstruction required, full weight bearing may take up to 2 to 3 months to occur, to allow for full healing of the bone.
2. AlMugaren, F. M., Pak, C. J., Suh, H. P. & Hong, J. P. Best Local Flaps for Lower Extremity Reconstruction. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open 8, e2774-8 (2020).
3. Muramatsu K, Ihara K, Doi K, Yoshida K, Iwanaga R, Hashimoto T, Taguchi T. Functional neuro-vascularized muscle transfer for oncological reconstruction of extremity sarcoma. Surg Oncol. 2012 Dec;21(4):263-8.
PATIENT STORIES
Post Massive Weight Loss Body Contouring
A 40-year-old lady consulted with Dr Pek with the desire to correct large amounts of excess skin and soft tissue. She had undergone Bariatric Surgery (Sleeve Gastrectomy) 2 years prior to her presentation and had successfully lost almost 30kg of weight. With ... Read more
Treating Gynecomastia – Correct Male Breasts through minimally invasive techniques
A 38-year-old male engineer presented to Dr Pek with symptomatic growth of his chest/breast area. Since puberty, he complained of unusually prominent chest tissue around his nipple and areolar region. This had worsened gradually over the years, with the left ... Read more
Upper eyelid lift and eyebags rejuvenation
63 years old Chinese female with hypertension and hyperlipidemia presented to Dr Pek with significant droopiness of her upper eyelids on both sides, affecting the upper portion of her visual field. She would constantly feel that her upper eyelids were heavy, ... Read more
Bilateral breast reconstruction using abdominal free flaps
A 45-year-old mother of 2 children was diagnosed with left breast cancer, for which a skin-sparing mastectomy (total removal of breast tissue leaving behind the skin envelope) was recommended. Read more
ARTICLES
Let's be real, we all have those areas of our body where ...
Rhinoplasty, commonly known as a nose job, is a surgical ...
Plastic reconstructive surgery is a specialised field that ...
Droopy eyelids are not just a cosmetic concern. While it ...
Contact Form
1 Orchard Boulevard #10-08 Camden Medical Centre, Singapore 248649
6 Napier Rd, #08-01 Gleneagles Medical Center, Singapore 258499
Tel: +65 6737 4565 | Mobile: +65 8828 4565 | Email: clinic@polarisplasticsurgery.com | Business Hours: Mon - Fri: 9am - 6pm | Sat: 9am - 1pm | Sun/Ph: Closed